
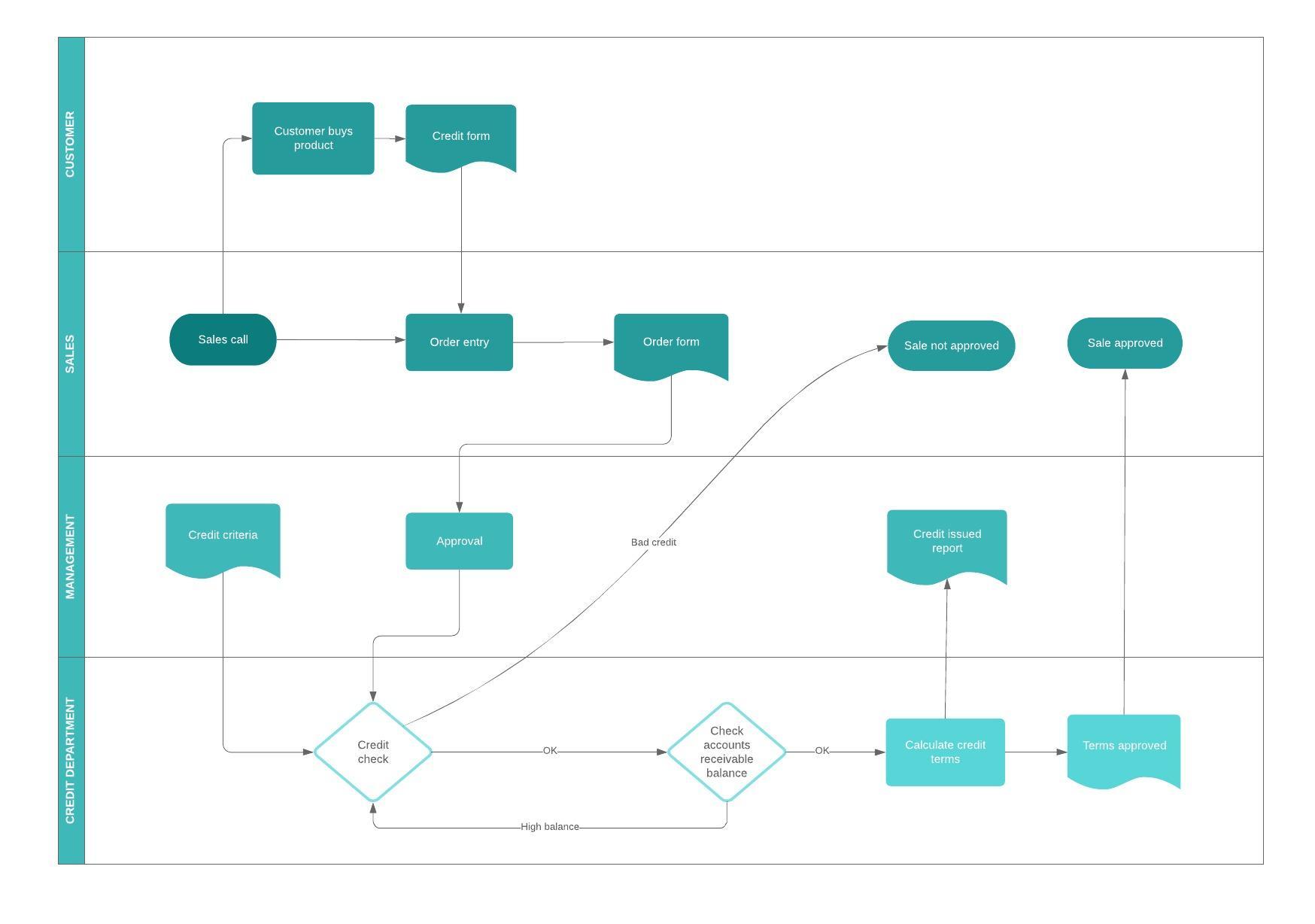
Process maps are based on employee reports, are created manually and provide higher-level views of workflows. Business process models shouldn’t be confused with process maps, another common type of business process diagram.Swimlanes are used to identify who owns which components of a process.Rectangles represent specific activities within a workflow.Ovals represent beginnings and endpoints of processes.Diamonds represent decision points or gateways.Within these notation systems, certain visual elements have universally recognized meanings when used in a process model. Whether an organization uses UML diagrams or BPMN diagrams, these standardized notation methodologies allow process models to be easily shared and read by anyone: Process models are typically rendered using one of two standardized styles of graphical business process notation: Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) - also called Business Process Model and Notation - or Unified Modeling Language (UML).A model could even help the company pinpoint the exact stage at which these drop-offs occur.
#Free business process modeling tools software#
For example, by creating a model of its new account creation process, a software company might discover that a significant number of customers are abandoning the sign-up process because it takes too long. Because process models are based on quantitative data, they offer genuinely objective views of workflows as they exist in practice, including key data, metrics or events that may have otherwise gone unnoticed.Rather, they are produced by data-mining algorithms that use the data contained within event logs to construct models of the workflows as they exist. Success and failure rates of the process.Timelines of the overall process and each step in the process.Decision points and the different paths workflows can take based on their outcomes.Who owns or initiates those events and activities.Events and activities that occur within a workflow.Process modeling generates comprehensive, quantitative activity diagrams and flowcharts containing critical insights into the functioning of a given process, including the following:

What is business process modeling?Ī business process model is a graphical representation of a business process or workflow and its related sub-processes. These process models help organizations document workflows, surface key metrics, pinpoint potential problems and intelligently automate processes. Even the business users directly involved in these processes may lack total transparency into exactly what happens at every step of the way.īusiness analysts can gain end-to-end views of the business process lifecycle through business process modeling, a business process management (BPM) technique that creates data-driven visualizations of workflows. If an organization wants research and development (R&D) investments to produce sufficient returns, IT issues resolved with minimal downtime or a highly accurate lead qualification workflow, it needs to understand these processes on an objective and comprehensive level. However, when they need to ensure that those processes consistently drive optimal outcomes, “a pretty good idea” isn’t enough. Most enterprises have a pretty good idea of the various business processes powering their daily operations. Business process modeling gives organizations a simple way to understand and optimize workflows by creating data-driven visual representations of key business processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
